Difference between revisions of "UDPTX"
(→DPDK) |
(→Performance) |
||
| (128 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
At this moment BrandMeister provides several backends (options) to send outgoing UDP: | At this moment BrandMeister provides several backends (options) to send outgoing UDP: | ||
* socket | * socket | ||
| − | * | + | * uring |
* AF_XDP | * AF_XDP | ||
* DPDK | * DPDK | ||
* Ixy | * Ixy | ||
| + | * verbs | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
== socket == | == socket == | ||
| − | This is standard default backend that uses Berkley sockets for sending a traffic. It tries to send the data in non-blocking mode and has special transmission thread to re-send failed packets. | + | This is standard default backend that uses Berkley sockets for sending a traffic. It tries to send the data in non-blocking mode and has special transmission thread to re-send failed packets or offload main thread on high load (> 50% CPU core). '''Not available in builds for Debian 12 and higher.''' |
=== You have to use it if you have === | === You have to use it if you have === | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
=== Performance === | === Performance === | ||
| − | Passed performance tests to transmit to | + | Passed performance tests to transmit to 20K connections |
=== Configuration === | === Configuration === | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
''transmitter = "socket";'' | ''transmitter = "socket";'' | ||
| − | == | + | == uring == |
| − | This is | + | This is standard default backend in '''builds for Debian 12 and higher'''. Uses Berkley sockets and io_uing Kernel API for sending a traffic. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=== Performance === | === Performance === | ||
| − | Passed performance tests to transmit to | + | Passed performance tests to transmit to 45K connections |
=== Configuration === | === Configuration === | ||
| − | ''transmitter = " | + | ''transmitter = "uring <module parameters>";'' |
| − | + | ==== Module parameters ==== | |
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | (-c) --core-count <n> - set count of workers (default is 2) | ||
| + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set buffer length to <n> slots (default is 512) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
== AF_XDP == | == AF_XDP == | ||
| − | This is faster forwarding backend that uses AF_XDP socket of Ethernet interface for sending a traffic and in most cases communicates directly with Linux network interface driver. | + | This is faster forwarding backend that uses AF_XDP socket of Ethernet interface for sending a traffic and in most cases communicates directly with Linux network interface driver. Due to monopolise NIC queues any configuration with multiple cores has to use ranges of queues per instance (for example: instance 1 uses 8 queues staring from 0 and instance 2 uses 8 queues starting from 8). |
=== Limitations === | === Limitations === | ||
| − | * | + | * Requires to use a single ethernet interface for BrandMeister's traffic (IPv4 and IPv6, local site connectivity will not work) |
| − | * | + | * All traffic will be routed via default gateway (except loopback, see next bullet) |
| + | * Loopback addresses (127.0.0.1 and ::1) are handled by using Berkley sockets | ||
* Interface have to be configured to use the same count of TX and RX queues (please read man ''ethtool'') | * Interface have to be configured to use the same count of TX and RX queues (please read man ''ethtool'') | ||
* May have compatibility problems (NIC may have no support of XDP) | * May have compatibility problems (NIC may have no support of XDP) | ||
| + | * On intel 10g nics (ixgbe) xdp tx works only if xdp rx is also enabled | ||
=== Performance === | === Performance === | ||
| − | Passed performance tests to transmit to | + | Passed performance tests to transmit to 55K connections |
=== Configuration === | === Configuration === | ||
| − | ''transmitter = "xdp:<interface name>";'' | + | ''transmitter = "xdp:<interface name> <module parameters>";'' |
''transmitter = "xdp:eth0";'' | ''transmitter = "xdp:eth0";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | (-w) --wakeup - use XDP in wakeup mode (XDP_USE_NEED_WAKEUP) | ||
| + | (-i) --in-flight <n> - set number of packets in flight (default value is calculated) | ||
| + | (-c) --core-ratio <n> - ratio between NIC queues and transmitting cores (instead of default value of 2) | ||
| + | (-f) --first-queue <n> - set number of first transmitting queue manually (default is 0) | ||
| + | (-q) --queue-count <n> - set transmission queue count manually (instead of all available queues) | ||
| + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) | ||
| + | (-r) --reference-interface <s> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: in case when you need to use VLANs, you have pass a physical interface (eth0 for example) as interface to bind and use '''--reference-interface''' key to pass the name of VLAN interface (eth0.1 for example) | ||
== DPDK == | == DPDK == | ||
| Line 75: | Line 92: | ||
=== Limitations === | === Limitations === | ||
| − | * | + | * All traffic will be routed via default gateway (except loopback, see next bullet) |
| + | * Loopback addresses (127.0.0.1 and ::1) are handled by using Berkley sockets | ||
* You have to have separate NIC or virtual detachable NIC port allowed to use for the DPDK transmission | * You have to have separate NIC or virtual detachable NIC port allowed to use for the DPDK transmission | ||
* Only DPDK port #0 will be used | * Only DPDK port #0 will be used | ||
| Line 83: | Line 101: | ||
=== Performance === | === Performance === | ||
| − | Passed performance tests to transmit to | + | Passed performance tests to transmit to 100K connections on '''ixgbe''' |
=== Configuration === | === Configuration === | ||
''transmitter = "Modules/DPDK-edge.so:<reference interface> <EAL parameters> [--] <module parameters>";'' | ''transmitter = "Modules/DPDK-edge.so:<reference interface> <EAL parameters> [--] <module parameters>";'' | ||
| − | ''transmitter = "Modules/DPDK-edge.so:eth0 - | + | ''transmitter = "Modules/DPDK-edge.so:eth0 -a 0000:af:00.0 --file-prefix bm --lcores '(0-8)@1,3,5,7,9' -- -c 1 -q 2048 -b 1 -l 4096";'' |
* Reference interface is a kernel attached interface used for normal communications (please read about raw mode). DPDK will reuse its IPs and default gateway | * Reference interface is a kernel attached interface used for normal communications (please read about raw mode). DPDK will reuse its IPs and default gateway | ||
* For EAL parameters please [https://doc.dpdk.org/guides/linux_gsg/linux_eal_parameters.html read this documentation] | * For EAL parameters please [https://doc.dpdk.org/guides/linux_gsg/linux_eal_parameters.html read this documentation] | ||
| − | * It will use so many NIC queues as defined amount of slave logical cores minus one | + | * It will use so many NIC queues as defined amount of slave logical cores minus one and multiplied by core ratio (so ratio means how may queues each core should handle) |
* The best performance on NUMA machines could be reached by using the same CPU as NIC connected by pinning logical cores via EAL's parameter ''lcores'' and BrandMeister's parameter ''affinity'' | * The best performance on NUMA machines could be reached by using the same CPU as NIC connected by pinning logical cores via EAL's parameter ''lcores'' and BrandMeister's parameter ''affinity'' | ||
* Also in [http://doc.dpdk.org/guides/linux_gsg/enable_func.html#running-dpdk-applications-without-root-privileges most cases it requires to run BrandMeister with root privileges], you can do this by overriding systemd configuration ([https://askubuntu.com/questions/659267/how-do-i-override-or-configure-systemd-services beandmeister@.service.d]): | * Also in [http://doc.dpdk.org/guides/linux_gsg/enable_func.html#running-dpdk-applications-without-root-privileges most cases it requires to run BrandMeister with root privileges], you can do this by overriding systemd configuration ([https://askubuntu.com/questions/659267/how-do-i-override-or-configure-systemd-services beandmeister@.service.d]): | ||
| Line 103: | Line 121: | ||
==== Module parameters ==== | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| − | + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | |
| − | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | + | |
| − | + | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | (-c) --core-ratio <n> - ratio between NIC queues and DPDK cores | + | (-c) --core-ratio <n> - ratio between NIC queues and DPDK cores (instead of default value of 4) |
(-q) --queue-size <n> - set PMD queue size to <n> slots (instead of automatically generated) | (-q) --queue-size <n> - set PMD queue size to <n> slots (instead of automatically generated) | ||
| − | + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 512) | |
| − | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of | + | |
(-p) --pthresh <n> | | (-p) --pthresh <n> | | ||
(-h) --hthresh <n> | PMD specific threshold values: | (-h) --hthresh <n> | PMD specific threshold values: | ||
| Line 124: | Line 139: | ||
=== Limitations === | === Limitations === | ||
| − | * Similar to DPDK but experimental | + | * Similar to DPDK but experimental |
| − | * | + | * Supports '''ixgbe''' and '''virtio''' only |
* Software CRC only | * Software CRC only | ||
| − | === | + | === Performance === |
| + | |||
| + | Passed performance tests to transmit 120K connections | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Configuration === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''transmitter = "Modules/Dixie.so:<reference interface> <PCI address> <module parameters>";'' | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | + | --core-ratio <n> | |
| + | --queue-size <n> | ||
| + | --queue-count <n> | ||
| + | --buffer-length <n> | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | ''transmitter = "Modules/Dixie.so:eth0 0000:af:00.0 --queue-count 8";' | |
| − | + | ||
| + | == verbs == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is method is only suitable when you use [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenFabrics_Alliance OFED/RDMA-enabled NIC], mostly [https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/ Mellanox and its OEM derives]. Both IP over Ethernet and IP over InfiniBand are supported. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Configuration === | ||
| + | ''transmitter = "verbs:<interface name> <module parameters>";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''transmitter = "verbs:rocep175s0 --reference-interface vlan100";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | --core-count <n> - set count of workers (default is 1) | ||
| + | --queue-size <n> - set queue size manually (default is 512) | ||
| + | --device-port <n> - device port (default is 1) | ||
| + | --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (default is 1024) | ||
| + | --reference-interface <ipoib0> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
= UDP Receiver = | = UDP Receiver = | ||
In reception part UDPTX's driver works in parallel with socket receiver. All it does, is accelerate reception of UDP packets on particular interface. | In reception part UDPTX's driver works in parallel with socket receiver. All it does, is accelerate reception of UDP packets on particular interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * socket (in dedicated thread) | ||
| + | * uring | ||
| + | * eBPF + AF_XDP | ||
| + | * eBPF + AF_XDP + XDPHelper | ||
| + | * verbs | ||
| + | |||
| + | == socket == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This method allows Core to offload main thread on high-loaded servers by reducing amount of system calls to receive UDP messages. '''Not available in builds for Debian 12 and higher.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Configuration === | ||
| + | ''receiver = "socket <module parameters>";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == uring == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This method allows Core to offload main thread on high-loaded servers by reducing amount of system calls to receive UDP messages. | ||
| + | '''Available in builds for Debian 12 and higher.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Configuration === | ||
| + | ''receiver = "uring <module parameters>";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set buffer length to <n> slots (default is 2048) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
== eBPF + AF_XDP == | == eBPF + AF_XDP == | ||
| Line 146: | Line 221: | ||
=== Limitations === | === Limitations === | ||
| − | * | + | * Hardware interface have to be configured to use the same count of TX and RX queues (please read man ''ethtool'') |
| − | + | * In case of VLANs it is possible to pass VLAN interface to get configuration from via parameter ''--reference-interface'' | |
* eBPF handles traffic '''before iptables''' | * eBPF handles traffic '''before iptables''' | ||
* Works with '''only a single instance''' of BrandMeister Core on the single machine | * Works with '''only a single instance''' of BrandMeister Core on the single machine | ||
| + | * When XDP TX and XDP RX are configured to use the same interface, values of parameters ''--first-queue'' and ''--queue-count'' will be reused from TX | ||
=== Configuration === | === Configuration === | ||
| − | ''receiver = "Modules/ExpressFilter.o:<interface name>";'' | + | ''receiver = "Modules/ExpressFilter.o:<interface name> <module parameters>";'' |
| − | ''receiver = "Modules/ExpressFilter.o:eth0";'' | + | ''receiver = "Modules/ExpressFilter.o:eth0 --reference-interface eth0.1";'' |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | (-w) --wakeup - use XDP in wakeup mode (XDP_USE_NEED_WAKEUP) | ||
| + | (-f) --first-queue <n> - set number of first receiving queue manually (default is 0) | ||
| + | (-q) --queue-count <n> - set receiving queue count manually (instead of all available queues) | ||
| + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) | ||
| + | (-r) --reference-interface <s> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: in case when you need to use VLANs, you have pass a physical interface (eth0 for example) as interface to bind and use '''--reference-interface''' key to pass the name of VLAN interface (eth0.1 for example) | ||
== eBPF + AF_XDP + XDPHelper == | == eBPF + AF_XDP + XDPHelper == | ||
| − | This is method is fully the same as eBPF + AF_XDP but uses small additional daemon XDPHelper to '''load and share eBPF program between several BrandMeister Core instances'''. XDPHelper is supplied with BrandMeister Core and starts automatically only when required (thanks to systemd and D-BUS activation). By default XDPHelper uses eBPF program ExpressFilter.o (see ''xdphelper.service''). | + | This is method is fully the same as eBPF + AF_XDP but uses small additional daemon XDPHelper to '''load and share eBPF program between several BrandMeister Core instances'''. This method also helps when NIC resets on eBPF load such as ''isgbe''. XDPHelper is supplied with BrandMeister Core and starts automatically only when required (thanks to systemd and D-BUS activation). By default XDPHelper uses eBPF program ExpressFilter.o (see ''xdphelper.service''). |
=== Limitations === | === Limitations === | ||
| − | * The same list of limitations as in case of eBPF + AF_XDP except support of multiple instances | + | * The same list of limitations as in case of eBPF + AF_XDP except support of multiple instances and eBPF preloading |
* All instances of BrandMeister Core should use the same network interface | * All instances of BrandMeister Core should use the same network interface | ||
| + | * Multiple instances only work on NICs with '''N-tuples''' or '''flow-control''' features | ||
=== Configuration === | === Configuration === | ||
| − | ''receiver = "xdp:<interface name>";'' | + | ''receiver = "xdp:<interface name> <module parameters>";'' |
| − | ''receiver = "xdp:eth0";'' | + | ''receiver = "xdp:eth0 --reference-interface eth0.1";'' |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | (-w) --wakeup - use XDP in wakeup mode (XDP_USE_NEED_WAKEUP) | ||
| + | (-f) --first-queue <n> - set number of first receiving queue manually (default is 0) | ||
| + | (-q) --queue-count <n> - set receiving queue count manually (instead of all available queues) | ||
| + | (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) | ||
| + | (-r) --reference-interface <s> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: in case when you need to use VLANs, you have pass a physical interface (eth0 for example) as interface to bind and use '''--reference-interface''' key to pass the name of VLAN interface (eth0.1 for example) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == verbs == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is method is only suitable when you use [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenFabrics_Alliance OFED/RDMA-enabled NIC], mostly [https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/ Mellanox and its OEM derives]. NIC should have support of Flow Steering. Both IP over Ethernet and IP over InfiniBand are supported. | ||
| + | In case of Ethernet card it should have N-tuples enabled ('''ethtool -K eth0 ntuple on'''). Mellanox Connectx cards need device managed flow steering (options mlx4_core log_num_mgm_entry_size=-1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Configuration === | ||
| + | ''receiver = "verbs:<interface name> <module parameters>";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''receiver = "verbs:rocep175s0 --reference-interface vlan100";'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Module parameters ==== | ||
| + | All these parameters are optional and override default settings | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | --queue-size <n> - set queue size manually (default is 512) | ||
| + | --reference-interface <eth0.1> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 10:26, 2 May 2023
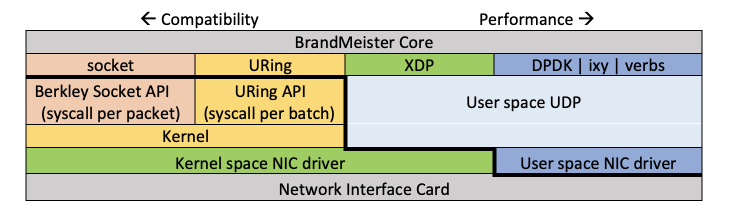
UDPTX is BrandMeister-own UDP communication library, used to transmit and receive UDP traffic fast. It is very important for BrandMeister to spend less time to send and receive packets, it makes transmission (and finally sound) more smooth.
Contents
UDP Transmitter
At this moment BrandMeister provides several backends (options) to send outgoing UDP:
- socket
- uring
- AF_XDP
- DPDK
- Ixy
- verbs
socket
This is standard default backend that uses Berkley sockets for sending a traffic. It tries to send the data in non-blocking mode and has special transmission thread to re-send failed packets or offload main thread on high load (> 50% CPU core). Not available in builds for Debian 12 and higher.
You have to use it if you have
- non-ethernet interfaces
- more than one interface for outgoing traffic (such as public + AMPR, or one for IPv4 and another one for IPv6)
- huge routing tables
Performance
Passed performance tests to transmit to 20K connections
Configuration
transmitter = "socket";
uring
This is standard default backend in builds for Debian 12 and higher. Uses Berkley sockets and io_uing Kernel API for sending a traffic.
Performance
Passed performance tests to transmit to 45K connections
Configuration
transmitter = "uring <module parameters>";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-c) --core-count <n> - set count of workers (default is 2) (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set buffer length to <n> slots (default is 512)
AF_XDP
This is faster forwarding backend that uses AF_XDP socket of Ethernet interface for sending a traffic and in most cases communicates directly with Linux network interface driver. Due to monopolise NIC queues any configuration with multiple cores has to use ranges of queues per instance (for example: instance 1 uses 8 queues staring from 0 and instance 2 uses 8 queues starting from 8).
Limitations
- Requires to use a single ethernet interface for BrandMeister's traffic (IPv4 and IPv6, local site connectivity will not work)
- All traffic will be routed via default gateway (except loopback, see next bullet)
- Loopback addresses (127.0.0.1 and ::1) are handled by using Berkley sockets
- Interface have to be configured to use the same count of TX and RX queues (please read man ethtool)
- May have compatibility problems (NIC may have no support of XDP)
- On intel 10g nics (ixgbe) xdp tx works only if xdp rx is also enabled
Performance
Passed performance tests to transmit to 55K connections
Configuration
transmitter = "xdp:<interface name> <module parameters>";
transmitter = "xdp:eth0";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-w) --wakeup - use XDP in wakeup mode (XDP_USE_NEED_WAKEUP) (-i) --in-flight <n> - set number of packets in flight (default value is calculated) (-c) --core-ratio <n> - ratio between NIC queues and transmitting cores (instead of default value of 2) (-f) --first-queue <n> - set number of first transmitting queue manually (default is 0) (-q) --queue-count <n> - set transmission queue count manually (instead of all available queues) (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) (-r) --reference-interface <s> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways
Note: in case when you need to use VLANs, you have pass a physical interface (eth0 for example) as interface to bind and use --reference-interface key to pass the name of VLAN interface (eth0.1 for example)
DPDK
This is fastest forwarding backend that uses kernel-bypass NIC driver for sending a traffic. It allows to save much more CPU time due to direct poll communications to the NIC and CRC offload features of some NIC models. In some tests we got up to 75% acceleration. List of supported NIC models can be found here.
Limitations
- All traffic will be routed via default gateway (except loopback, see next bullet)
- Loopback addresses (127.0.0.1 and ::1) are handled by using Berkley sockets
- You have to have separate NIC or virtual detachable NIC port allowed to use for the DPDK transmission
- Only DPDK port #0 will be used
- We added support of dpdk-proc-info and dpdk-pdump
- Very hard in configuration and performance tuning!
Performance
Passed performance tests to transmit to 100K connections on ixgbe
Configuration
transmitter = "Modules/DPDK-edge.so:<reference interface> <EAL parameters> [--] <module parameters>";
transmitter = "Modules/DPDK-edge.so:eth0 -a 0000:af:00.0 --file-prefix bm --lcores '(0-8)@1,3,5,7,9' -- -c 1 -q 2048 -b 1 -l 4096";
- Reference interface is a kernel attached interface used for normal communications (please read about raw mode). DPDK will reuse its IPs and default gateway
- For EAL parameters please read this documentation
- It will use so many NIC queues as defined amount of slave logical cores minus one and multiplied by core ratio (so ratio means how may queues each core should handle)
- The best performance on NUMA machines could be reached by using the same CPU as NIC connected by pinning logical cores via EAL's parameter lcores and BrandMeister's parameter affinity
- Also in most cases it requires to run BrandMeister with root privileges, you can do this by overriding systemd configuration (beandmeister@.service.d):
# /etc/systemd/system/brandmeister@.service.d/override.conf [Service] User=root
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-c) --core-ratio <n> - ratio between NIC queues and DPDK cores (instead of default value of 4) (-q) --queue-size <n> - set PMD queue size to <n> slots (instead of automatically generated) (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 512) (-p) --pthresh <n> | (-h) --hthresh <n> | PMD specific threshold values: (-w) --wthresh <n> | https://doc.dpdk.org/guides/prog_guide/poll_mode_drv.html#configuration-of-transmit-queues (-r) --rs-thresh <n> | (-f) --free-thresh <n> | (-s) --software-crc - force software CRC calculation
Ixy
Ixy is very experimental and light user-space network driver. At this moment it supports Intel 82599ES family (aka Intel X520) and virtio. Please read Ixy documentation.
Limitations
- Similar to DPDK but experimental
- Supports ixgbe and virtio only
- Software CRC only
Performance
Passed performance tests to transmit 120K connections
Configuration
transmitter = "Modules/Dixie.so:<reference interface> <PCI address> <module parameters>";
--core-ratio <n> --queue-size <n> --queue-count <n> --buffer-length <n>
transmitter = "Modules/Dixie.so:eth0 0000:af:00.0 --queue-count 8";'
verbs
This is method is only suitable when you use OFED/RDMA-enabled NIC, mostly Mellanox and its OEM derives. Both IP over Ethernet and IP over InfiniBand are supported.
Configuration
transmitter = "verbs:<interface name> <module parameters>";
transmitter = "verbs:rocep175s0 --reference-interface vlan100";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
--core-count <n> - set count of workers (default is 1) --queue-size <n> - set queue size manually (default is 512) --device-port <n> - device port (default is 1) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (default is 1024) --reference-interface <ipoib0> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways
UDP Receiver
In reception part UDPTX's driver works in parallel with socket receiver. All it does, is accelerate reception of UDP packets on particular interface.
- socket (in dedicated thread)
- uring
- eBPF + AF_XDP
- eBPF + AF_XDP + XDPHelper
- verbs
socket
This method allows Core to offload main thread on high-loaded servers by reducing amount of system calls to receive UDP messages. Not available in builds for Debian 12 and higher.
Configuration
receiver = "socket <module parameters>";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024)
uring
This method allows Core to offload main thread on high-loaded servers by reducing amount of system calls to receive UDP messages. Available in builds for Debian 12 and higher.
Configuration
receiver = "uring <module parameters>";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-l) --buffer-length <n> - set buffer length to <n> slots (default is 2048)
eBPF + AF_XDP
This is modern method to accelerate UDP reception in BrandMeister Core. It allows to save up to 30% CPU time.
Limitations
- Hardware interface have to be configured to use the same count of TX and RX queues (please read man ethtool)
- In case of VLANs it is possible to pass VLAN interface to get configuration from via parameter --reference-interface
- eBPF handles traffic before iptables
- Works with only a single instance of BrandMeister Core on the single machine
- When XDP TX and XDP RX are configured to use the same interface, values of parameters --first-queue and --queue-count will be reused from TX
Configuration
receiver = "Modules/ExpressFilter.o:<interface name> <module parameters>";
receiver = "Modules/ExpressFilter.o:eth0 --reference-interface eth0.1";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-w) --wakeup - use XDP in wakeup mode (XDP_USE_NEED_WAKEUP) (-f) --first-queue <n> - set number of first receiving queue manually (default is 0) (-q) --queue-count <n> - set receiving queue count manually (instead of all available queues) (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) (-r) --reference-interface <s> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways
Note: in case when you need to use VLANs, you have pass a physical interface (eth0 for example) as interface to bind and use --reference-interface key to pass the name of VLAN interface (eth0.1 for example)
eBPF + AF_XDP + XDPHelper
This is method is fully the same as eBPF + AF_XDP but uses small additional daemon XDPHelper to load and share eBPF program between several BrandMeister Core instances. This method also helps when NIC resets on eBPF load such as isgbe. XDPHelper is supplied with BrandMeister Core and starts automatically only when required (thanks to systemd and D-BUS activation). By default XDPHelper uses eBPF program ExpressFilter.o (see xdphelper.service).
Limitations
- The same list of limitations as in case of eBPF + AF_XDP except support of multiple instances and eBPF preloading
- All instances of BrandMeister Core should use the same network interface
- Multiple instances only work on NICs with N-tuples or flow-control features
Configuration
receiver = "xdp:<interface name> <module parameters>";
receiver = "xdp:eth0 --reference-interface eth0.1";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
(-w) --wakeup - use XDP in wakeup mode (XDP_USE_NEED_WAKEUP) (-f) --first-queue <n> - set number of first receiving queue manually (default is 0) (-q) --queue-count <n> - set receiving queue count manually (instead of all available queues) (-l) --buffer-length <n> - set workers buffer length to <n> slots (instead of default value of 1024) (-r) --reference-interface <s> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways
Note: in case when you need to use VLANs, you have pass a physical interface (eth0 for example) as interface to bind and use --reference-interface key to pass the name of VLAN interface (eth0.1 for example)
verbs
This is method is only suitable when you use OFED/RDMA-enabled NIC, mostly Mellanox and its OEM derives. NIC should have support of Flow Steering. Both IP over Ethernet and IP over InfiniBand are supported. In case of Ethernet card it should have N-tuples enabled (ethtool -K eth0 ntuple on). Mellanox Connectx cards need device managed flow steering (options mlx4_core log_num_mgm_entry_size=-1)
Configuration
receiver = "verbs:<interface name> <module parameters>";
receiver = "verbs:rocep175s0 --reference-interface vlan100";
Module parameters
All these parameters are optional and override default settings
--queue-size <n> - set queue size manually (default is 512) --reference-interface <eth0.1> - reference interface to monitor routes, gateways
 BrandMeister
BrandMeister